The process of homeostasis maintains a steady internal milieu. So how is it possible for adaptations to occur? What are the internal mechanisms that determine a good outcome versus a negative one?
Changes in the external environment, such as exercise training, challenge homeostasis, producing spatial and temporal responses in the internal environment. These cause interactions between muscle, bone and gut, modulated by the Endocrine system. The degree and nature of these responses dictate whether a positive adaptation occurs. An excessive response, or a response not in tune with the networks of the Endocrine system, can hinder adaptation or produce a maladaptive response. The balance and interplay of internal responses are crucial in determining the outcome to exercise training in the individual.
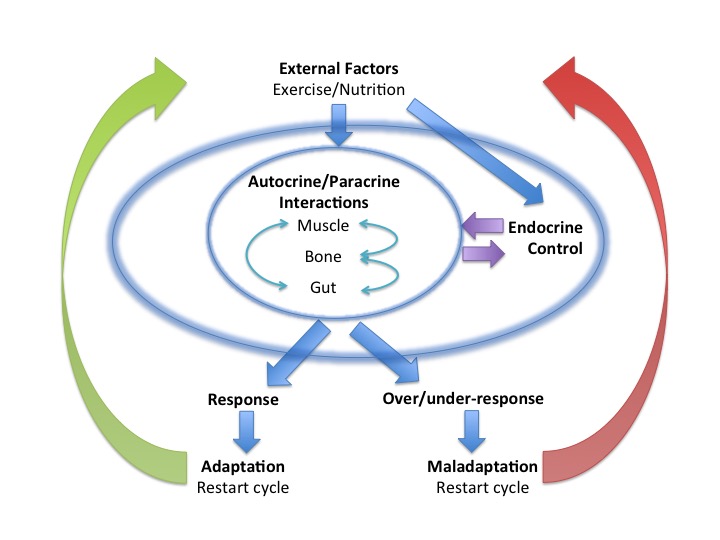
Local responses in exercising tissues
Exercising tissues release exerkines (metabolites, nucleic acids, peptides) which are packaged in exosomes and microvesicles. The content of these vesicle packages increases with intensity of endurance exercise in a dose-dependent manner. These exerkines have autocrine and paracrine effects, which modulate systemic adaptations to endurance exercise in the tissues themselves and those in the vicinity.
The range of these molecular responses from exercising tissues has been identified applying multi-omics (epigenomic, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses). Furthermore variance in trainability has been shown to be correlated with the integrated responses of tissue molecular signalling pathways to endurance exercise.
In a similar manner, the degree of inflammatory response and production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) to exercise mediate favourable adaptations. Inter-individual variations in redox status has been shown to determine the ability to adapt to exercise training. However, unlimited increase in response does not necessarily produce a better outcome. An over response to exercise in these signalling pathways, hinders adaptation.
Exercise promotes bone adaptation in terms of bone material, structure and muscle action. Paracrine crosstalk occurs between muscle and bone. Muscle myokines and insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1) favour bone formation, whilst inflammatory molecules, such as interleukin 6 (Il-6) released during muscle contractions, favour bone reabsorption. The balance between these opposing processes determines whether bone remodelling is effective, or whether bone stress reactions occur over a pathological continuum. These responses and adaptations occur on the background of lifespan Endocrine environment, which impacts the outcome.
Gut microbiota
The gut microbiota support the regulation of inflammation at the local and systemic level. Furthermore the communication between the gut microbiota and mitochondria has been described as an important interaction in facilitating adaptive responses to exercise. Mitochondria are organelles crucial for production of ATP, as well as RONS. The gut microbiota are involved in mitochondrial biogenesis by regulating key mitochondrial transcriptional factors and enzymes . Furthermore, the metabolites of the gut microbiota such as short chain fatty acids, modulate the inflammatory effects of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Conversely genetic variants in the mitochondrial genome could impact mitochondrial function and thus the gut microbiota in terms of composition and activity.
The gut microbiota have a role in regulating intestinal permeability. Leaky gut is where epithelial integrity is lost at the tight junctions between cells in the gut lining. Leaky gut can occur in gut dysbiosis and also following endurance exercise where re-perfusion injury produces acute hyper-permeability. In these instances, increased gut permeability augments the antigen load and causes increased systemic inflammation and potentially can trigger autoimmune disease. This demonstrates that an excessive inflammatory response to exercise can hinder positive adaptation
Metabolic adaptations
Metabolic flexibility, the ability to respond and adapt to changes in metabolic demand, is enhanced with exercise training through these autocrine, paracrine and Endocrine mechanisms. Metabolic flexibility supports energy availability and fuel selection during exercise. Exercise mimetics, such as artificial metabolic modulators, have been reported to up-regulate gene expression to shift metabolism to fat oxidation in exercising muscle. This would potentially extend the limit of endurance exercise. However this “short cut” to adaptation favouring improved sport performance is illegal, with such molecular ligands on the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) banned list.
Hierarchy of control
There is a hierarchy of control in modulating multi-system adaptations to exercise. The Endocrine system is key. Exercise per se produces an Endocrine response, for example exercise is a key stimulus for growth hormone release via the hypothalamus, the neuroendocrine gatekeeper. Growth hormone supports the anabolic response to exercise. In addition, the Endocrine milieu during the lifespan has an impact on response and adaptations to exercise. Any disruption in the Endocrine system hinders adaptive changes. Endocrine dysfunction may occur as a result of non-integrated periodisation of exercise/nutrition and recovery as seen in relative energy deficiency in sports (RED-S). Dysfunction can also occur due to an Endocrine pathology.
Conclusion
Changes in external stimuli, such as exercise and nutrition, produce internal responses on autocrine, paracrine and Endocrine levels. These molecular signalling pathways drive adaptive changes through integrated, network effects. However any imbalances in these interactive responses can hinder desired adaptive changes and even result in negative maladaptive outcomes to exercise training.
For further discussion on Endocrine and Metabolic aspects of SEM come to the BASEM annual conference 22/3/18: Health, Hormones and Human Performance
References
Keay N, Logobardi S, Ehrnborg C, Cittadini A, Rosen T, Healy ML, Dall R, Bassett E, Pentecost C, Powrie J, Boroujerdi M, Jorgensen JOL, Sacca L. Growth hormone (GH) effects on bone and collagen turnover in healthy adults and its potential as a marker of GH abuse in sport: a double blind, placebo controlled study. Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 85 (4) 1505-1512. 2000.
Sport Endocrinology presentations
Sports Endocrinology – what does it have to do with performance? Dr N.Keay, British Journal of Sport Medicine
Balance of recovery and adaptation for sports performance Dr N.Keay, British Association of Sport and Exercise Medicine
Inflammation: Why and How Much? Dr N.Keay, British Association of Sport and Exercise Medicine
Clusters of Athletes – A follow on from RED-S blog series to put forward impact of RED-S on athlete underperformance Dr N.Keay, British Association of Sport and Exercise Medicine
Optimal Health: For All Athletes! Part 4 – Mechanisms Dr N.Keay, British Association of Sport and Exercise Medicine
The potential of endurance exercise-derived exosomes to treat metabolic diseases Nature Reviews Endocrinology
Exosomes as Mediators of the Systemic Adaptations to Endurance Exercise Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine
Genomic and transcriptomic predictors of response levels to endurance exercise training
Journal of Physiology
Adaptations to endurance training depend on exercise-induced oxidative stress: exploiting redox inter-individual variability Acta Physiologica
Mechanical basis of bone strength: influence of bone material, bone structure and muscle action Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions
The Crosstalk between the Gut Microbiota and Mitochondria during Exercise Frontiers in Physiology
Leaky Gut As a Danger Signal for Autoimmune Diseases Frontiers in Immunology
Metabolic Flexibility in Health and Disease Cell Metabolism
Hormones and Sports Performance
PPARδ Promotes Running Endurance by Preserving Glucose Cell Metabolism
14 thoughts on “Endocrine system: balance and interplay in response to exercise training”